Department of Cell Biology

At NYU Langone’s Department of Cell Biology our goal is to advance knowledge and understanding of fundamental biological processes, from the level of the genome to that of cells, tissues, and organisms. We employ cutting-edge technologies to investigate cell structure and function, intercellular communication, signal transduction, cell migration, signaling between organs, and the response of cells to the environment. Our faculty work with an array of model systems to best address scientific questions in stem cell biology, developmental biology, neurobiology, immunology, genetics, epigenetics, and cancer.
We are committed to excellence and innovation in an environment that values curiosity, creativity, and collaboration. Our interdisciplinary research brings together basic scientists and clinical faculty to make discoveries that not only expand our knowledge of biology but contribute to ameliorating human disease.
Contact Us
Our laboratories and offices are located in multiple NYU Langone research facilities, which include the Medical Science Building and the Joan and Joel Smilow Research Center, both located at 540 First Avenue, the Science Building at 435 East 30th Street, and the Alexandria Center for Life Sciences at 430 East 29th Street.
For general inquiries, email Jenny Wong, assistant director of research operations, at ChanYing.Wong@NYULangone.org.
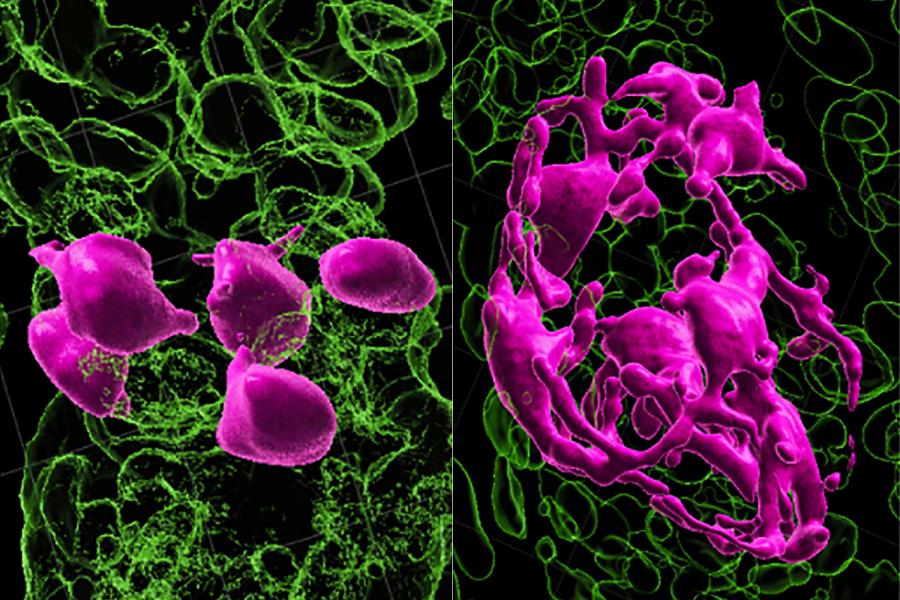
Pulses of RhoA Signaling Stimulate Actin Polymerization and Flow in Protrusions to Drive Collective Cell Migration
Read More
Transcription Factor RORa Enforces Stability of the Th17 Cell Effector Program by Binding to a Rorc Cis-Regulatory Element
Read More
A RORγt+ Cell Instructs Gut Microbiota-Specific Treg Cell Differentiation
Read More
Microbial Byproducts and Reproductive Fitness
Read More
Our Training Programs

Our Faculty

Our Publications

Our Research

Related News

New Approach May Counter Autoimmunity

Mechanism Rewires Metabolism for Weight Loss

Immune Cell Could Help Explain—& Temper—Food Allergies

Immune Cell Type Is Key to Understanding Food Allergies

Key Brain Chemical Can ‘Pause’ Pregnancy After Conception

Study Suggests Why Cancer Therapy Boosts Heart Disease Risk

Studies Show Cell Changes in Pig Heart & Kidney Transplants

Gene Therapy May Slow Life-Threatening Heart Condition
Cells Move Differently in Groups
Discovery May Help Gauge Efficacy of Future Cancer Vaccines

Blood Cancer Pilot Grants Support Translational Research