
Cerebral Oxygen Monitoring: Electroencephalography & Cerebral Oximetry
We are the first research team in the world to investigate the potential benefits of using both cerebral oximetry and electroencephalography (EEG) during cardiopulmonary resuscitation to provide more robust information about the magnitude of ischemia in the brain. While brain oximetry measures the amount of oxygen reaching the brain, EEG can inform us as to whether oxygen that has been delivered to the brain of individual patients has enabled the brain to function again. In a cohort of 16 patients, we demonstrated that combining these monitoring techniques to more precisely measure resuscitation quality is feasible.
Moreover, we propose that using cerebral oximetry and EEG together may assist physicians in determining optimal care for each individual. For example, real-time EEG data may enable refined decision-making by providing guidance regarding the oxygen levels needed to bring back a patient with a minimum of brain damage. Whereas 60 percent may be the ideal average, by monitoring changes in brain activity as compared to cerebral oxygenation, physicians can determine if more or less oxygen is needed depending on how long the patient has been without circulation. This is particularly important since every patient is different.
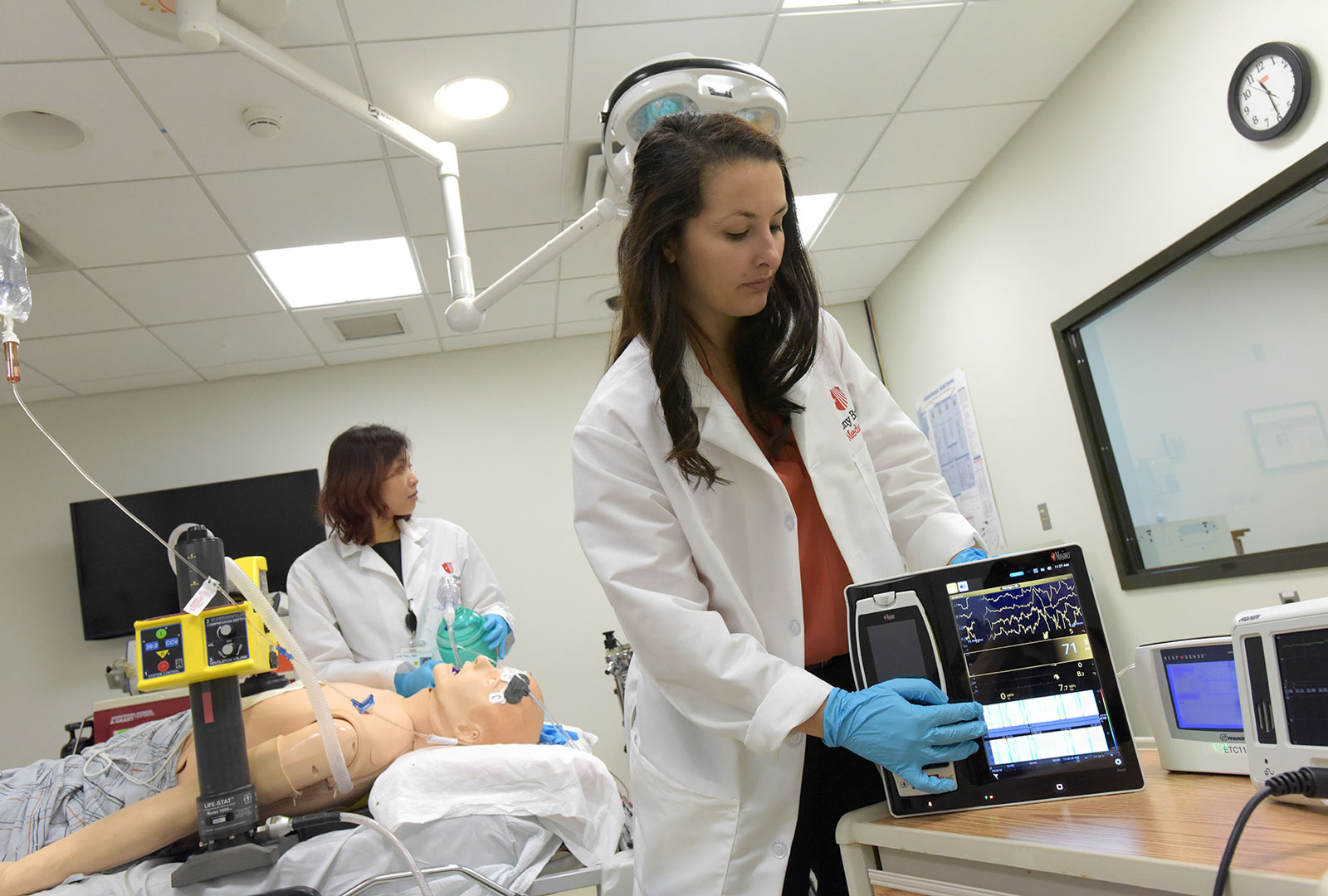

Learn more about our study combining EEG and cerebral oximetry. Opens in a new tab. Opens in a new tab.